Stacking is a complicated topic, and warrants its own technical note. Which stacking features are available and how they work depends which modes you are in. There are three main mode “groups”: SAVE, CORRELATION, AND STACK. Within those are sub modes whose names indicate their function.
Save
- Autosave
- Manual Save
Correlation
- No correlation
- Standard correlation
- Stack before Correlation
- Stack after Correlation
- Random Source Correlation
Stack
- Autostack
- Replace
There is a complicated interplay between the above modes and between these modes and the stack options:
- Stack polarity
- Display Intermediate Stacks
- Unstack Delay
- Each shot is automatically stacked
- Each stacked record is displayed as the stack count increments
- The stack count continues to increment with each shot until you clear the data, even if you save the data sometime in the process.
- Each shot is automatically stacked until the Stack Limit is reached.
- When the Stack Limit is reached, the data are saved automatically.
- Data are automatically cleared and the stack count is reset to one the next time the seismograph triggers after saving the data.
- Stack Polarity is generally left set to Positive.
- Displaying intermediate stacks is optional. Disabling this option results in faster production, since the data do not need to be sent over the network with every stack.
- Each shot is automatically stacked until the Stack Limit is reached.
- When the Stack Limit is reached, the data are saved automatically.
- Data are automatically cleared and the stack count is reset to one the next time the seismograph triggers after saving the data.
- Data are stacked in raw, uncorrelated form in the Geodes, and are not sent to the PC until the Stack Limit is reached.
- When the Stack Limit is reached, the stacked raw record is correlated in the Geode (with the most recent pilot), sent to the PC, and saved.
- Each shot is automatically stacked until the Stack Limit is reached.
- When the Stack Limit is reached, the data are saved automatically.
- Data are automatically cleared and the stack count is reset to one the next time the seismograph triggers after saving the data.
- Each individual record is correlated with its own pilot and stacked in correlated form in the Geodes.
- Displaying intermediate, correlated stacks is optional.
- When the Stack Limit is reached, the stacked, correlated record is sent to the PC and saved.
- Each stack is replaced by the previous. If Auto Save is not enabled, the previous stack is lost.
- If Auto Save is on the Stack Limit is hard-coded to 1.
- Each shot is displayed.
We will examine each possible combination in rough order of popularity
Modes: Manual save , No correlation, Autostack
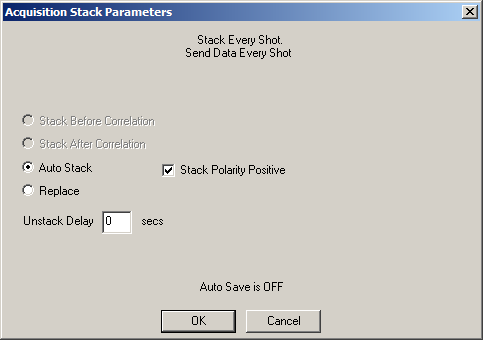
This is the most common configuration used in refraction and downhole surveys.
Stack Polarity can be changed at any time. This is most often used in shear wave surveys where reverse-polarity stacking is required.
Unstack Delay gives you the option to unstack the most recent stack; for example, setting the stack count from 4 back to 3. The data will be held in a temporary buffer for n seconds, during which time you can choose whether to stack or not. If you do nothing, the data will be automatically stacked after n seconds, and unstacking will be no longer be an option for that stack. If Unstack Delay is set to zero, this feature is disabled.
Modes: Auto Save, No correlation, Autostack
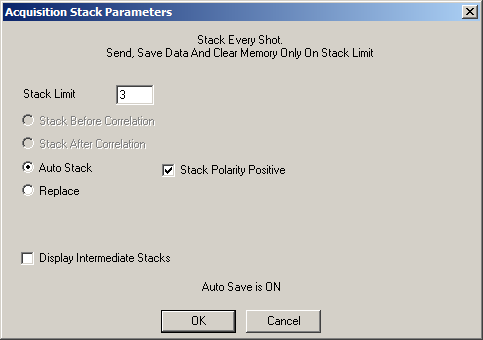
This is the most common configuration used in impulsive reflection surveys.
Modes: Auto Save, Standard Correlation, Stack Before Correlation
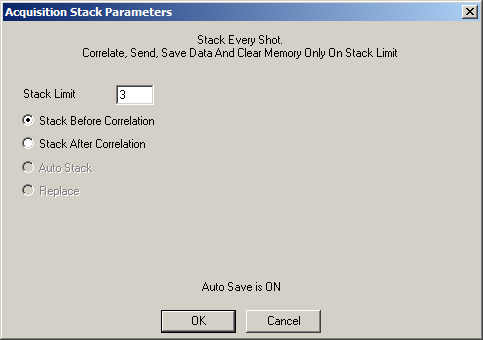
This is the most common configuration used in swept-source reflection surveys.
Modes: Auto Save, Standard Correlation, Stack After Correlation
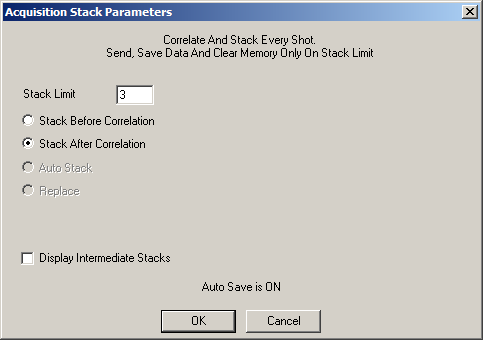
This is the most common configuration used in Random Source (mini-Sosie) reflection surveys.
Modes: Auto Save, Replace
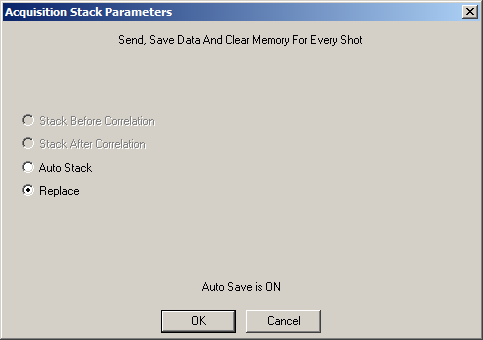
This is the most common configuration used in Continuous Recording surveys.
